Jun 3rd 2022
Did you know fat is a MUST in the human diet—and should be about 20-35% of your daily calorie intake ? Of course, some fats are healthier than others. Today we’ll look at some of the best fats for wellness: Omega-3 fatty acids.
What is an Omega-3 Supplement?
Your body needs Omega-3 fatty acids to function, but the body cannot make Omega-3 fatty acids on its own. In general, we need to get Omega-3 fatty acids from food. You can also take an Omega-3 supplement as a reliable way to get these good fats into your routine. Omega-3 supplements are typically in the form of softgels, capsules, gummies, or liquids.
As you’re researching supplements, you’ll probably notice there
are
several
types of Omega-3s
. Here are three main ones (we’ll get into more details
below!):
- ALA—alpha-linolenic acid
- DHA—docosahexaenoic acid
- EPA—eicosapentaenoic acid
Benefits of Omega-3s
So, what is Omega-3 good for? Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly DHA and EPA, are found to have a number of critical benefits.
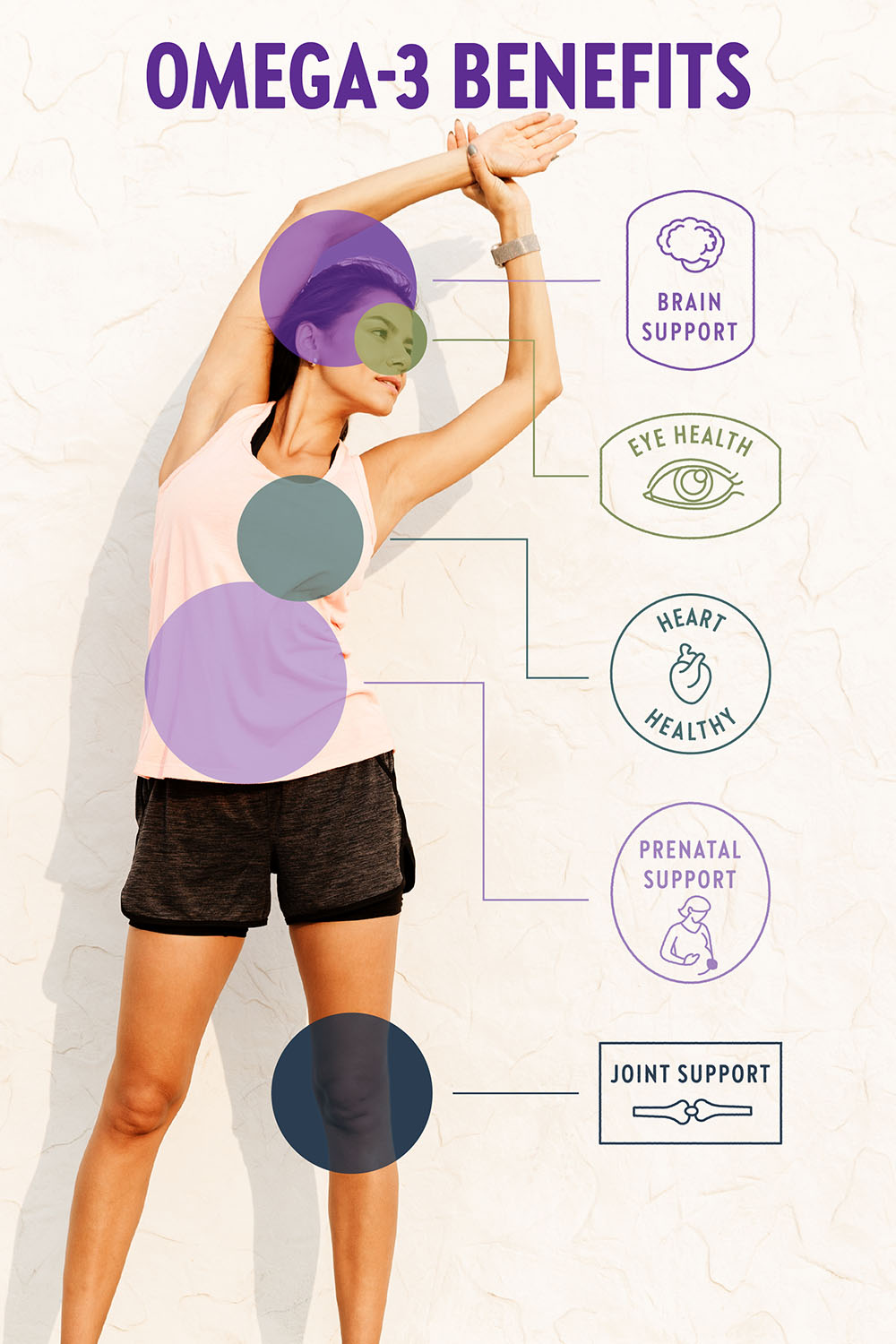
1. Heart Support
Omega-3s have been linked to significant benefits for heart and blood vessel health . These include reducing triglycerides in the blood and slowing the buildup of plaque on artery walls.
2. Brain Support
Researchers have studied the benefits of Omega-3s for brain health across age groups—including in young adults, pregnant mothers, and older adults. In general, DHA and EPA intake has been linked to improved cognitive function and brain health support .
3. Joint Support
Omega-3s have been researched for helping with joint health support .*
4. Eye Support
The retina of the eye is partly made up of Omega-3 fatty acids, specifically DHA. Researchers have suggested that taking Omega-3s can help support eye health .
5. Pregnancy & Lactation Support
For women who are expecting a baby or breastfeeding, Omega-3 fatty acids help support baby’s visual and cognitive development. The important fatty acids a mother consumes help to form the functional tissue of her baby’s brain. Omega-3s from mom pass to her baby both during pregnancy and during lactation.
Where Do Omega-3s Come From?
Beneficial Omega-3s have two main sources —from plants and from the sea.
1. Plant Omegas
ALA is a plant-derived Omega-3 found in oils of certain nuts and seeds, such as flaxseed oil and canola oil.
2. Marine Omegas
EPA and DHA are found in marine animals, such as fish or krill (tiny crustaceans that are food for penguins and whales). However, these sea animals actually do not synthesize their own Omega-3 (similar to us humans!). They get it from their own diet. The original sources of marine Omega-3s are microalgae.

You may be wondering, which is the best Omega-3? One thing to keep in mind is that DHA and EPA are more researched for their health benefits . When you consume ALA, the body can convert it to DHA and EPA, but the conversion rate is relatively limited. So, you may want to go directly for DHA and EPA.
Can Vegans Take Omega-3 Supplements?
The short answer: yes! There are definitely Omega-3 supplements for vegans . To get the equivalent good fats that you’d get from fish, vegans can opt for Omega-3 straight from the microalgae that are the potent, original source of EPA and DHA. Just be sure to read labels to make sure the product is 100% vegan—like our Vegan Omega-3 Complex .
How Much Omega-3 Should You Take?
Omega-3s do not have a recommended intake or assigned % Daily Value like some vitamins or minerals. Nutrition experts recommend eating smart by choosing more unsaturated “good” fat options in your day (see foods with Omega-3 listed below to help). Limit or avoid saturated fat and trans fats, which are linked to heart disease. Furthermore, the American Heart Association suggests having 2 servings of fatty fish per week to ensure you’re getting those critical Omega-3s. Microalgae oil is another way to get the same Omega-3s that we treasure in fish. Talk to your healthcare professional about how to choose the right omega-3 supplement for you.
Which Foods Have Omega-3s?
Wondering which plants, which fish, or which nuts have Omega-3s your body needs? Grab your shopping list and we’ll break it down!
Some common foods that provide dietary ALA :
- Flaxseeds (ground) or flaxseed oil
- Chia seeds
- Walnuts
- Soy foods
- Canola oil
Some common foods that provide dietary DHA and EPA :
- Salmon
- Mackerel
- Anchovies
- Sardines
- Trout
- Cod
- Shellfish (shrimp, crab, clam, oyster)
Choosing a Quality Omega-3 Supplement
Our family of Omega-3 products has something for everyone. We source the finest quality ingredients on earth and formulate products your body can really absorb. Ask yourself the following questions to pinpoint the perfect Omegas for you!
Want clinically studied whole fish oil with 17 Omegas, including essential DHA & EPA? Then Wholemega Fish Oil is perfect. This 2-gram daily dose of extra-virgin Wild Salmon oil is the equivalent of eating 3 servings of Salmon per week. (It also comes in easy-to-swallow Tiny Caps™.)
Want that same heart-healthy fish oil in an easy one-daily maintenance dose? Check out our Omega-3 Complex.
How about a purely vegan option, with naturally concentrated DHA & EPA from fermented microalgae ? Our Vegan Omega-3 Complex is for you. It’s a one-daily dose and delivers more of these key Omegas per gram than our fish oil!
Are you pregnant or planning to be? Moms-to-be can get prenatal DHA and EPA in a tiny, easy-to-swallow size with Wholemega Fish Oil for Moms. Or go straight for the naturally concentrated source of those Omegas with Prenatal Vegan Omega-3 Complex, formulated with potent microalgae oil.
New Chapter is here to help keep your wellness goals going strong, including getting excellent quality good fats like DHA and EPA into your day. We’re here to do wellness well, so you can do you!










